Android 获取子 View 的位置及坐标的方式
本文共 2626 字,大约阅读时间需要 8 分钟。
一、View
1.1、View 概述
视图 (View) 是一个容器,专门负责布局。表现为显示在屏幕上的各种视图,如 TextView、LinearLayout 等。
1.2、View 分类
View 主要分为两类,具体如下表格所示:
| 类别 | 示例 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 单一视图 | 即一个 View,如 TextView、EditText | 不包含子View |
| 视图组 | 即多个 View 组成的 ViewGroup,如 RelativeLayout | 包含子View |
1.3、View 类简介
-
View 类是 Android 中各种组件的基类;
-
View 的构造函数有四个,具体如下所示:
public View(Context context) {}public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0);}public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { this(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, 0);}public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {} -
源码中 View 的构造函数
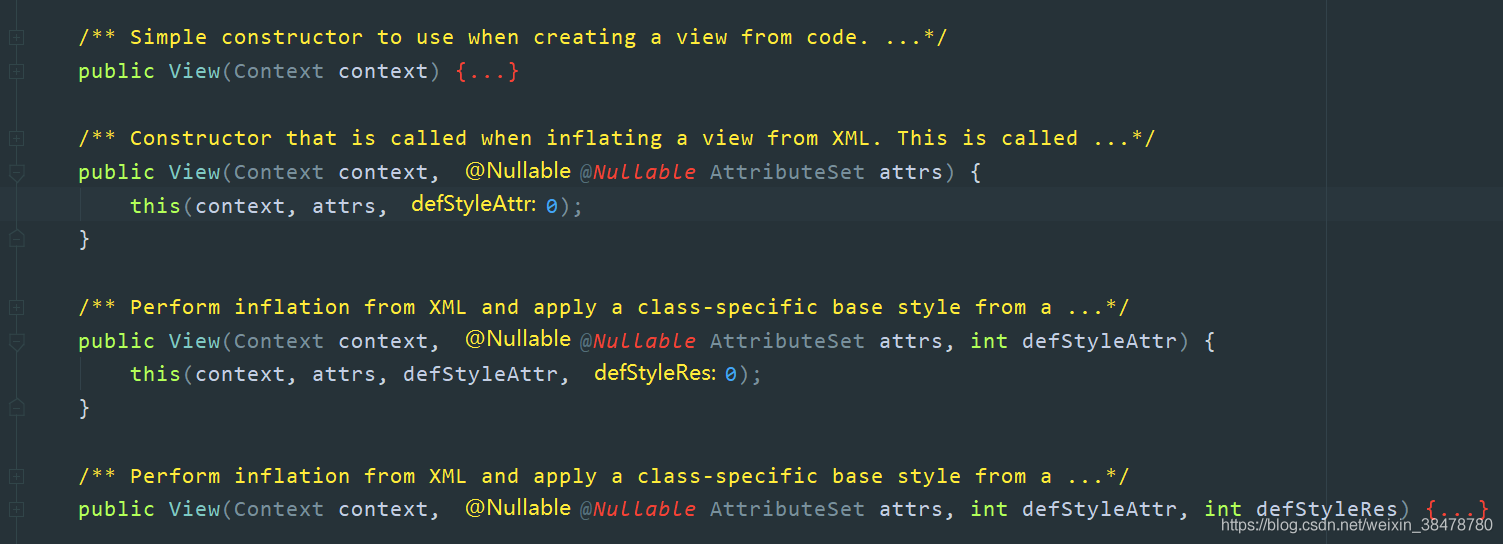
通过源码的注释我们可以看出:
- 如果 View 是在 Java 代码里面 new 的,则调用第一个构造函数–>View(Context);
- 如果 View 是在 xml 里声明的,则调用第二个构造函数–>View(Context, AttributeSet)。
二、Android 坐标系
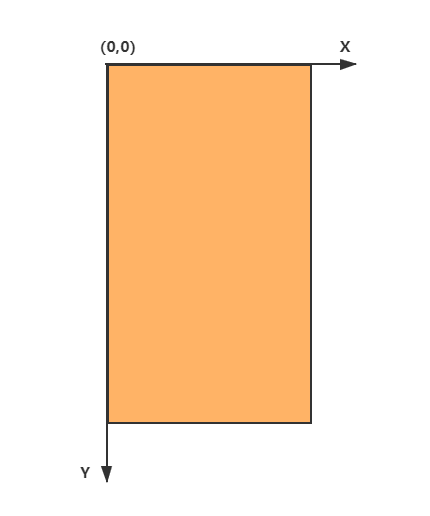
Android 坐标系和数学上的坐标系是不一样的,定义如下:
- 屏幕的左上角为坐标原点。
- 向右为 x 轴增大方向。
- 向下为 y 轴增大方向。
具体如下图所示:
三、View 的位置
View 的位置是相对于父控件而言的,由 4 个顶点确定,如下图 A、B、C、D 所示: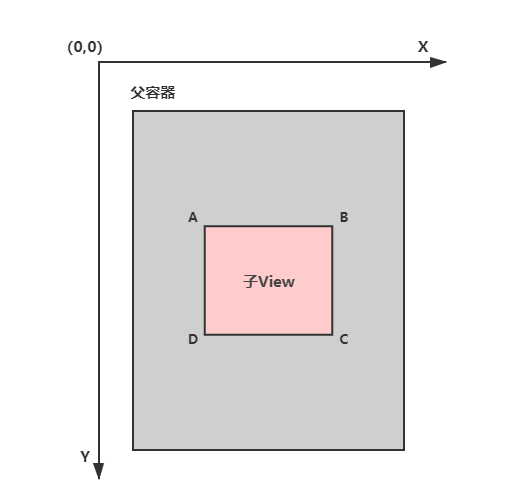
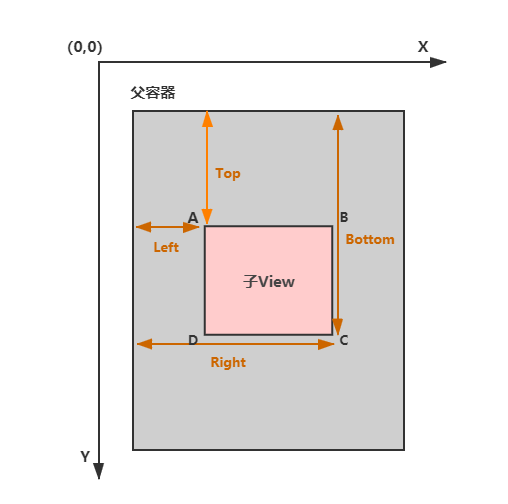
确定 View 的位置有四个参数,分别是 Top、Bottom、Left、Right:
- Top:子 View 左上角距父 View 顶部的距离。
- Left:子 View 左上角距父 View 左侧的距离。
- Bottom:子 View 右下角距父 View 顶部的距离。
- Right:子 View 右下角距父 View 左侧的距离
具体如下图所示:
四、获取 View 位置的方式
View 的位置是通过 getTop()、getLeft()、getBottom()、getRight() 函数进行获取的。
这里我写了一个小例子来演示这四个方法,如下所示:(获取内部子 View 的位置)

因为是为了演示 View 的位置,所有我这里用绝对布局,并且大小的单位都是用 px,具体布局如下所示:
我们现在用四个方法来获取一下 View 的位置,具体代码如下所示:
public class CoordinateActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private View mView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_coordinate); rl1 = findViewById(R.id.rl_1); mView = findViewById(R.id.view); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { MyLogUtils.i(mView.getTop() + "--Top --mView"); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getBottom() + "--Bottom --mView"); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getLeft() + "--Left --mView"); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getRight() + "--Right --mView"); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getX() + "--X --mView"); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getY() + "--Y --mView"); } }, 200); }} 打印结果如下所示:
最外层紫色的 View 的坐标是(200,200),大小是 600px,在它内部,有一个大小为 300px 的子 View 位于其中心位置,所以上述打印结果是完全正确的。
注意:
- 我这里调用 getTop() 等方法是在 onResume() 里面,并且延时了 200ms,是因为如果不延迟直接调用,会出现 View 还没有绘制完,所以获取到的位置都是 0,所以就用最简单的延迟处理了一下(这里的处理方法有很多,比如 View.post() 等);
- getX() 和 getY() 的意思是获取子 View 相对父容器的坐标,所以这里结果都是 150。
最后
小编在这将自己收集的一份《Android核心知识汇总》分享给大家,希望能对大家有所帮助。请点击获取。 喜欢本文的话,不妨顺手给我点个小赞、评论区留言或者转发支持一下呗~

转载地址:http://isxtz.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
nessus快速安装使用指南(非常详细)零基础入门到精通,收藏这一篇就够了
查看>>
Nessus漏洞扫描教程之配置Nessus
查看>>
Nest.js 6.0.0 正式版发布,基于 TypeScript 的 Node.js 框架
查看>>
nestJS学习
查看>>
NetApp凭借领先的混合云数据与服务把握数字化转型机遇
查看>>
NetBeans IDE8.0需要JDK1.7及以上版本
查看>>
netcat的端口转发功能的实现
查看>>
netfilter应用场景
查看>>
netlink2.6.32内核实现源码
查看>>
Netpas:不一样的SD-WAN+ 保障网络通讯品质
查看>>
NetScaler的常用配置
查看>>
netsh advfirewall
查看>>
NETSH WINSOCK RESET这条命令的含义和作用?
查看>>
Netstat端口占用情况
查看>>
Netty WebSocket客户端
查看>>
netty 主要组件+黏包半包+rpc框架+源码透析
查看>>
Netty 异步任务调度与异步线程池
查看>>
Netty中集成Protobuf实现Java对象数据传递
查看>>
Netty事件注册机制深入解析
查看>>
Netty原理分析及实战(四)-客户端与服务端双向通信
查看>>